Chapter 2: What Makes a High-Quality Backlink?
Links that come from more authoritative and relevant sites are referred to as high-quality backlinks.
They tend to pass Link Juice and help with overall SEO strategy.
Link Juice/ Equity
Link juice is the value and authority passed from one site to another via backlinks.
The higher the quality of a backlink, the more link juice you get.
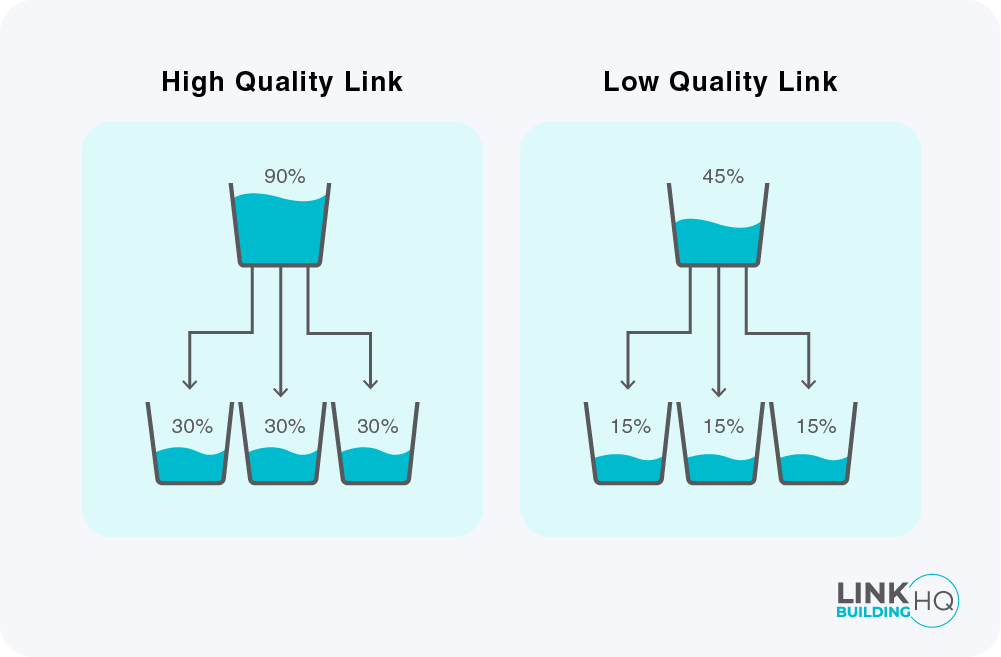
Now, all backlinks do not provide the same value. Some backlinks tend to have more power than others, depending on the source of the link.
Experts suggest that there is no one fixed ingredient that makes a perfect link. Rather, it is a mix of different factors that create a high-quality backlink.
What makes a High-Quality Backlink
We have divided these factors into two categories:
- Major factors are contextual, such as Relevance and Authority.
- Minor factors are technical, such as the anatomy of a backlink, including URL and anchor text.
Let’s look at the major ones..
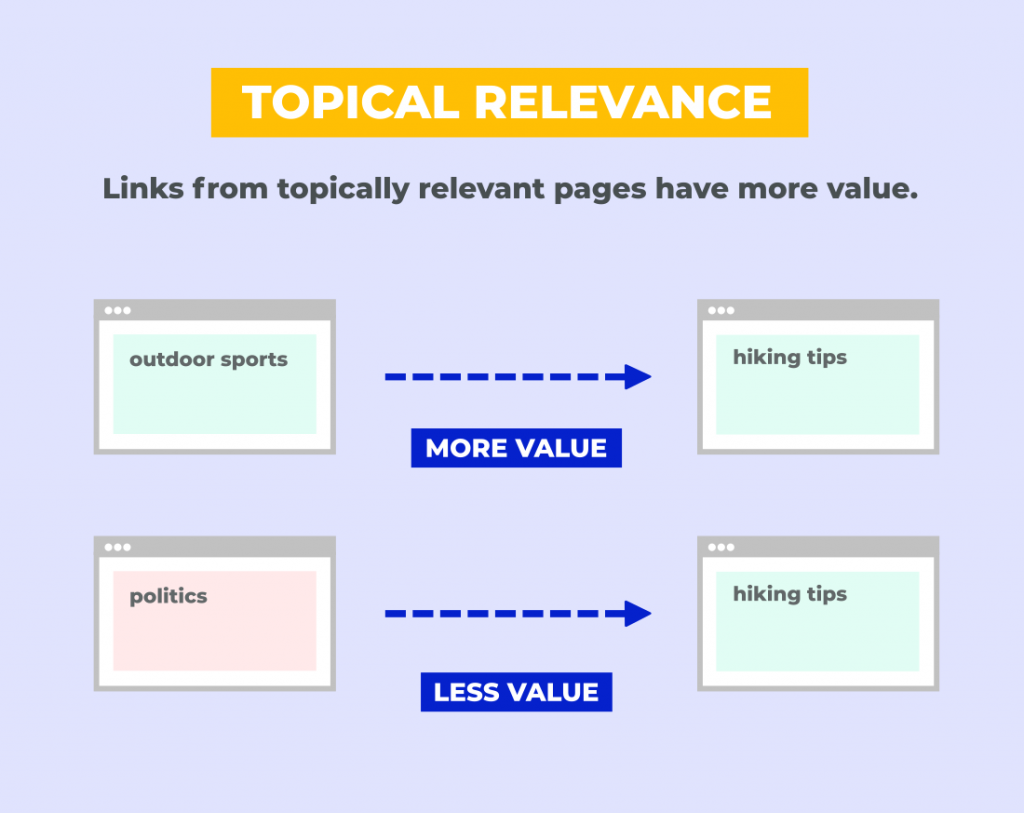
Relevance
Backlinks that are coming from another site or webpage must be related to your website in terms of its niche or content.
Imagine if you’re the owner of a small restaurant in Kent and you are looking to establish a digital presence for your business. Would you like to get a link from an article called ‘The Top 10 Budget-Friendly Restaurants in Kent’ or ‘Top 10 New Netflix Releases’?
This is precisely what relevance is all about. However, the relevance is two-tiered: Domain Relevance and Page Relevance.
1) Domain Relevance
Domain Relevance refers to how the niches of both websites are related. The one giving the link and the one getting the link.
For example, your restaurant’s website gets two links. One from National Geographic and another from Food Network. Which link do you think will have more worth? Answer: The latter will have more worth due to higher Domain Relevance than the former.
Domain relevance can be further broken down industry-wise.
- Direct Industry Relevance refers to the same niche and similar context.
For example, Your restaurant is getting mentioned by Food Network. - Indirect Industry Relevance refers to a different niche but similar context.
For example, your restaurant is getting mentioned by Booking.com.
How is it indirectly related? People who travel always look for places to dine in.
2) Page Relevance
It refers to the relevance of content on the two web pages.
For instance, National Geographic’s blog called ‘Understanding Cultures Through Food’ will have less page relevancy to your restaurant business than Food Network’s blog called ‘10 Must-Visit Restaurants in Kent City’.
On the page level, there is another factor called Keyword Cluster, which considers the relevance of keywords on both pages.
Authority
Authority is defined as the ability of search engines to trust or rely on your website.
Now, Google doesn’t provide clear guidelines on how it calculates Authority. But tools like SEMrush, Moz, and Ahref have developed scoring systems that predict the ranking of your site based on various factors.
Authority is divided into two major types:
1) Website Authority
Website Authority is a score that determines the ability of a website to rank on search engines.
It can range from 1 to 100. The higher the score, the better the site will rank on search engines.
2) Webpage Authority
A Webpage Authority is a score that assesses the ability of a webpage to rank on search engines.
Now before moving towards minor factors, let us dissect the backlink and take a closer look.
The three tools, i.e., Moz, SEMrush, and Ahref, have their own terms to define the concepts.
| Moz | Semrush | Ahref | |
| Website | Domain Authority | Authority Score | Domain Rating |
| Webpage | Page Authority | Page Score | URL Rating |
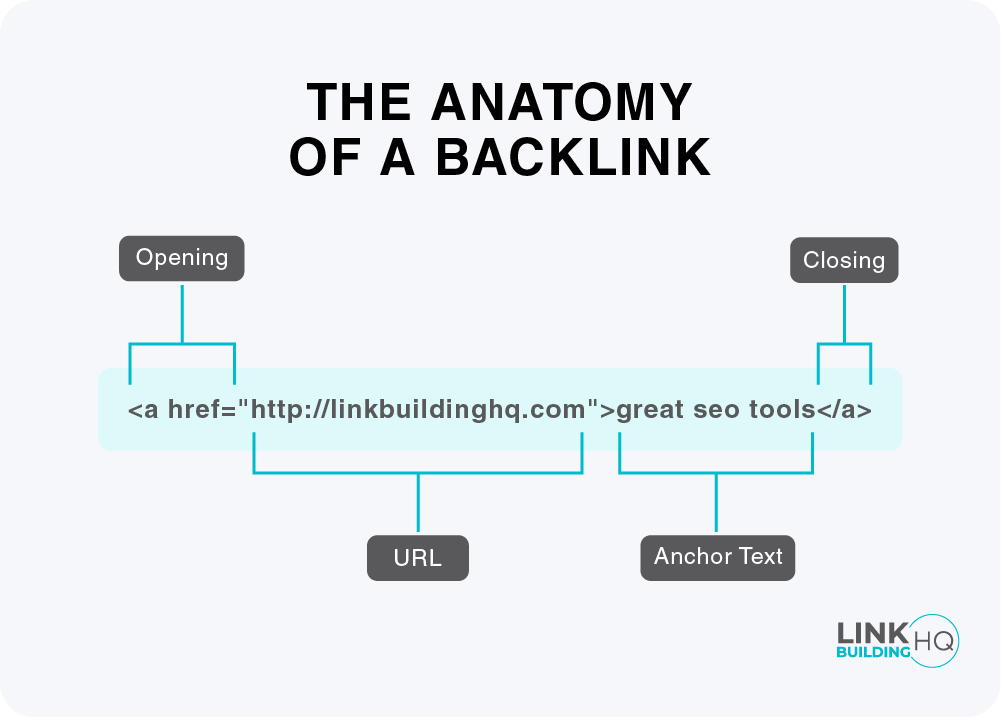
Backlink Anatomy
Typically, a backlink looks like this.
Confused? No worries, let us take one concept at a time.
Anchor Text
Ever noticed the clickable words while reading online blogs and articles?
That is exactly what anchor text is. The text (also known as a hyperlink) that has a link embedded into it is known as Anchor Text.
In SEO, anchor text placed contextually helps a backlink become more relevant.
For instance, the anchor text in the example above says ‘small business health insurance exchange’.
When Google reads this, it would probably think, ‘Okay, so the link must be about small business health insurance, and then assesses the mentioned page.
If the link was about the given topic, bravo! You made your link contextually relevant.
But if not, it will be considered irrelevant and consequently become Spammy.
Spammy links usually come from low-quality and irrelevant sites. They are also termed as Toxic Links or Unnatural links”.
There are two anchor text strategies that could help your backlink profile
- Link Placement
- Link Co-Occurrences
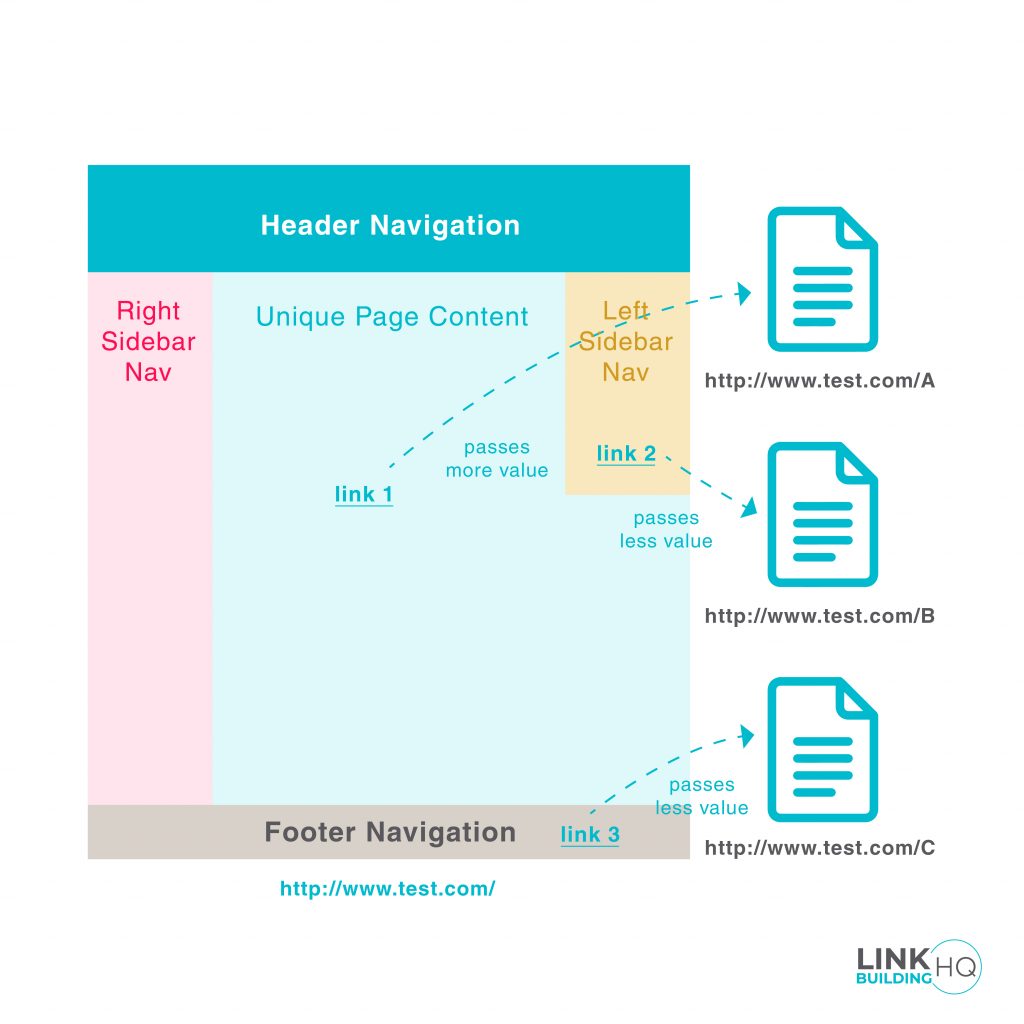
Link Placement
So, where is your link placed?
Is it embedded in the center of the blog or stashed away in the sidebar?
Because the positioning of the anchor text also contributes to deciding the ranking of your page.
Links that are contextually placed in a writeup garner more clicks and eventually better ranking than links that are stuffed in a footer.
Link Co-Occurrences
Text that surrounds the link or anchor text is known as Co-occurrence.
Co-occurrences are also termed as ‘baby anchor text’ as they elucidate more details about the link.
Co-occurrences are particularly more insightful for search engines when the anchor text is generic. For example: ‘click here ‘for more information, and so on.
Do you know which type of link actually passes the link juice? If not, continue reading.
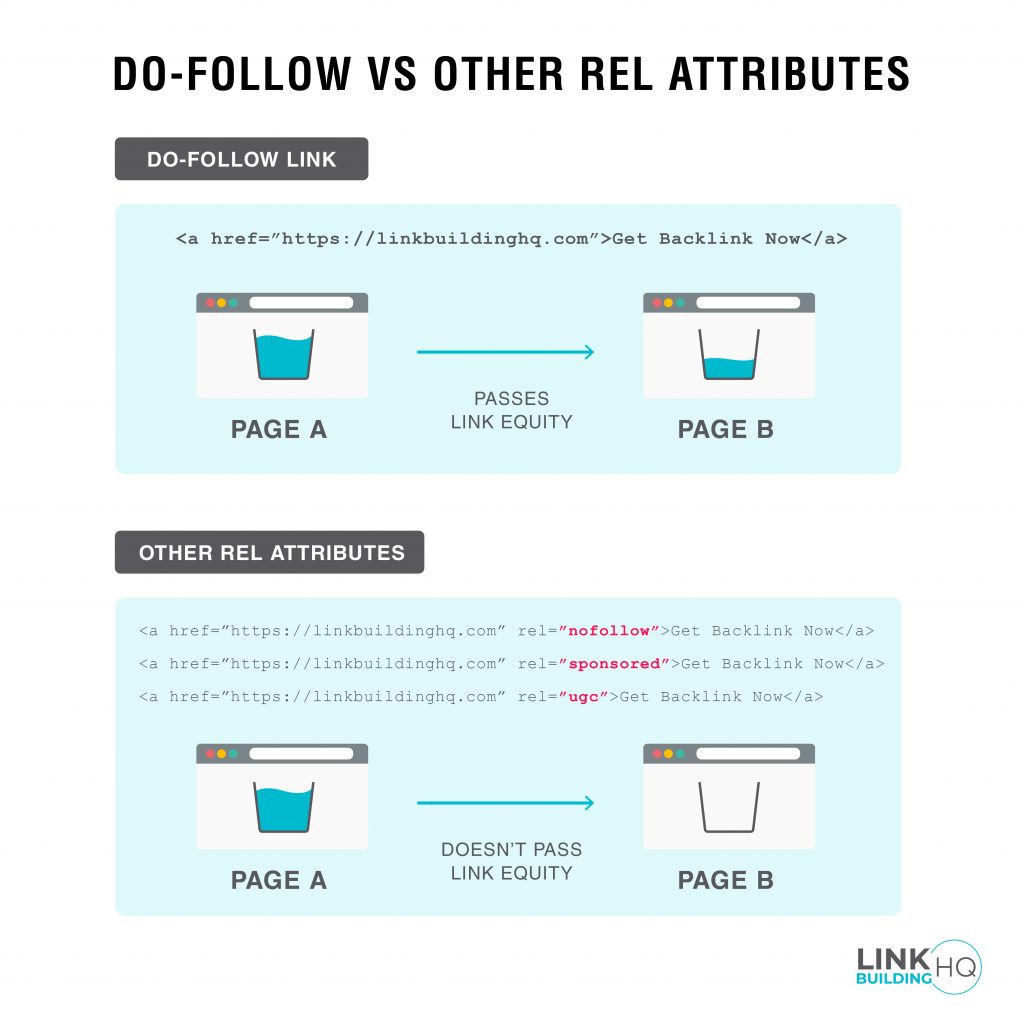
Do-Follow Link
Do-follow links act as the vote or endorsement for better rankings on search engines.
Also, these links are responsible for passing the link juice from the origin site to the destination site.
This is the HTML code of a do-follow link:
<a href=”http://raventools.com”>great SEO tools</a>
If your link looks like this, it is a do-follow link that passes the desired link juice.
Example: Any webpage link with the intent of quoting or citing useful information
By now, we have already established that not all links are equal. Some links pass the required link juice, and some do not.
Links that do not pass any link juice have a piece of code attached to them that indicates to Google that the two sites are not naturally linked.
Hence, Google returns without any evaluation whenever it sees that code.
That piece of code is called Rel Attribute.
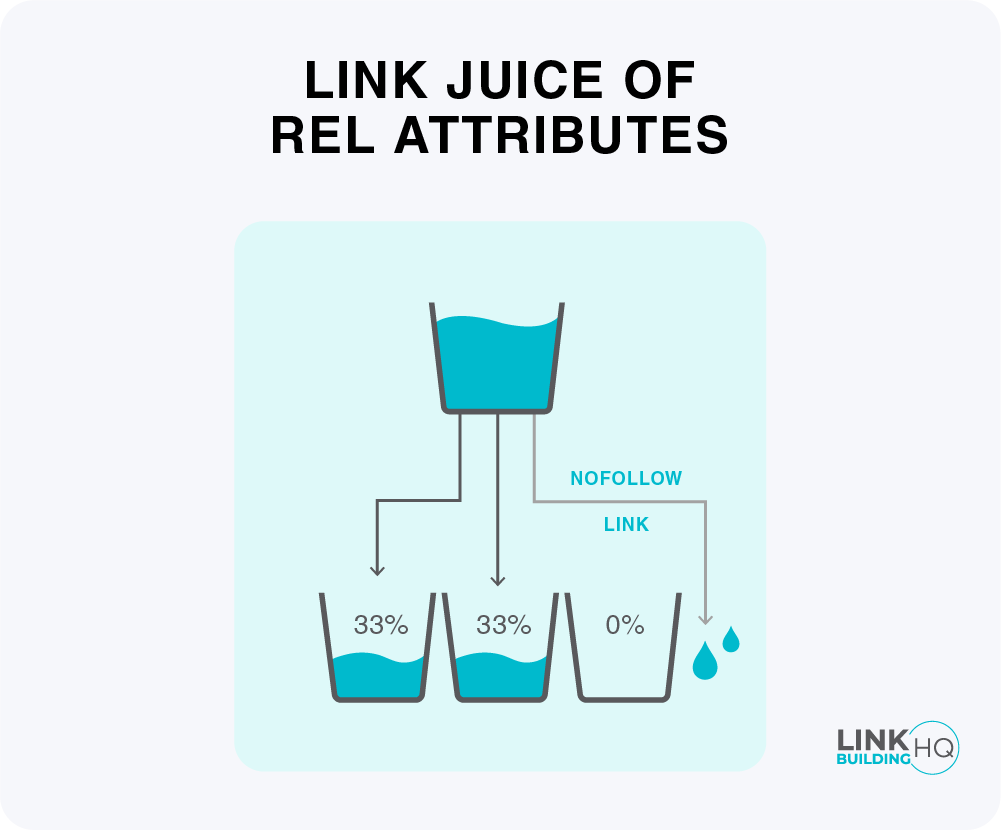
Link Rel Attribute
Rel Attribute in a link is a tiny piece of code that shows the relationship between the page a link is on and the page it is pointing to.
Here are three types of Rel Attributes.
1) No-Follow
<a href=”https://www.example.com” rel=”nofollow”>example link</a>
If your link contains ‘no follow’, it doesn’t count as vote or endorsement, and doesn’t pass any link juice.
Example: Any webpage link without the intent of endorsing the referenced link
2) Sponsored
<a href=”https://www.example.com” rel=”sponsored”>example link</a>
If your link contains ‘sponsored’, it intends to directly generate revenue and doesn’t pass any link juice.
Example: Sponsored ads, paid links, or affiliate links
3) User-Generated Content (UGC)
<a href=”https://www.example.com” rel=”ugc”>example link/a>
If your link contains ‘UGC’, it suggests that links are placed by any user and don’t pass any link juice.
Example: User comments on blogs, forums, and other pages.
Here is a snapshot of the differences between Do-Follow and other Rel Attributes.
| Do-Follow | No-Follow/UGC/Sponsored | |
| Definition | Links that direct crawlers to the mentioned webpage. | Links that inform crawlers to not to follow the mentioned webpage |
| Link Juice | Links that pass the link juice | Links that do not pass the link juice |
| Benefit | Benefit: Directly passes the link juice that helps in improving the rank. | Benefit: Organic traffic and brand recognition |
Many new sites usually use this technique to get a higher ranking in a short span of time. However, Google’s Penguin algorithm is developed solely to cater to this problem.
What Makes a High-Quality Backlink in a Nutshell?
To conclude everything above, here is what makes a high-quality backlink.
- The link should be coming from a high-authority page
- The link should be coming from a relevant niche
- The link should have relevant anchor text
- The link should be placed contextually in the middle of the page
- The link should be do-follow
- The link should be short and have relevant keywords.
So, does that mean all the backlinks should be high-quality? No, they should look natural.
What is a Natural Backlink Profile?
A backlink profile is a collection of links that are identified through various characteristics.
A Natural Backlink Profile should have diversified attributes and shouldn’t try to focus only on high-quality backlinks.
A natural backlink profile should have the following:
- A blend of links from high and low-authority websites.
- Anchor text ratio to be diverse with 50% branded keywords.
- New referring domains should be more than lost referring domains
- Links from more unique domains rather than from one domain.
- Links are diversified to home pages, services pages, and blog pages.
Moreover, the ratio between do-follow links and no-follow links should also be natural.
You can do that by adopting various link-building strategies and tactics.
Let’s talk about them in the next chapter.
Further Readings
- What is the Ideal Do-follow and No-follow Ratio?
- Link Equity: How To Determine An Actual Value Of A Link?
- What Happens If I Build A Bad Backlink?
- What Are The Characteristics Of A Healthy Link Profile?
- Links For Inner Pages Are Irrelevant Compared To Those For The Homepage
- Debunking The Common Myths In Link Building
- How To Be A Successful Link Builder