Google continuously improves its ranking algorithm to reshuffle the indexed pages and surface relevant content at the top. Some of these updates are more widespread than others, with their impact spanning across a large number of websites. These are called the broad core updates.
According to Google’s official update release dashboard, about 9-10 updates are reported every year. But among them, only three to four are the broader core updates carrying a bigger impact on search engine rankings.
What Is A Broad Core Update?
A core update refers to a series of major changes Google makes to its algorithm. These updates are released every three to four months and can have a significant impact on the broader ranking charts. Google describes them as:
“Several times a year, Google makes significant, broad changes to our search algorithms and systems. We refer to these as core updates.”
Essentially, they work like a self-cleaning mechanism where the system recognizes low-quality sites and pushes them down the SERPs. Besides other things, broad core updates can hit:
- Sites abusing their policies
- Sites providing no value to readers
- Spammy sites
- Websites operating on black hat SEO tactics
- Sites with unnatural backlinks
On the other hand, websites focusing on search intent, evergreen content, and organic link building are spared in the process. And even rewarded for helping users rather than gaming the algorithm and hogging undeserved traffic.
What is the Impact of A Google Core Update?
Fluctuations across the SERPs are common during a core update, but it doesn’t mean that sites are selectively targeted. It’s just how Google reassesses the algorithm and makes alterations to help users find sites with authoritative content and valuable assets.
However, it makes sense if you, as an SEO, panic at the thought of a broad core update. The impact can be extensive and sometimes unpredictable. It might haul you up at lightning speed or throw a site down in the dumps. But Google also said previously that:
“…most sites don’t need to worry about core updates and may not even realize one has happened.”
Counterpoint: *Sites creating helpful, reliable, and people-first content.
Sometimes, a core update may diminish the positive effects of a ranking signal that was previously functional. This doesn’t mean you’re doing anything wrong, but just that the ranking signal no longer contributes to your page’s performance. And thus the drop.
Broad core updates are designed to overhaul the search engine, resulting in notable ranking changes for websites. This is contradictory to named updates that are accompanied by targeted action. For example, the Penguin update targeted webspam, including sites using manipulative link tactics. During its 2012 rollout, many sites using artificially curated link profiles faced a major drop in visibility and traffic. Today, the update continues to be part of Google’s core algorithm but no longer causes manual penalties.
Occasionally, Google uses core updates to introduce new features on the search engine results pages. For example, tweaking or removing alternative listings or restructuring the SERP layout. In some updates, the Knowledge Panel saw new features, while others were characterized by a more focused approach to optimize listings in the PAA section.
How to Track Core Update Impact & Recover From It?
We get it; getting hit by a core update feels like being run over by a bulldozer. But there are ways to avoid a coma. First and foremost, confirm that the core update has finished rolling out. Next, follow our step-wise approach to unlock gaps in your strategy and find recovery methods.
Review Traffic Drop
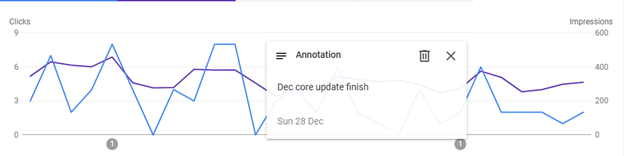
The first indication of negative impact is declining traffic. You’ll see it on your GSC dashboard, and it helps to add annotations at the start and end of the update.
Compare the traffic pattern a week before and after the broad core update to see if there was a drop caused by it. This will make it easier to correlate the traffic drop with the release of an update.
How to Fix It?
If the traffic went down but there’s no notable change in impressions, it might be minor fluctuations. But it’s best to assess which pages lost most traffic and track them to ensure the trend doesn’t continue.
For major flatlines in traffic, review all existing content on the website and check if it serves user intent and matches guidelines for authoritative content. For sites facing significant drops, creating EEAT-based content can help. Use these self assessment questions to analyze if your content meets the standards required to maintain rankings.
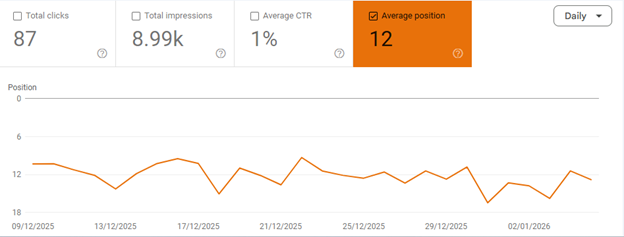
Assess Position Drop
A major drop in ranking positions will be reflected in the top pages and queries section of your search console. For a broader picture, filter the performance report by “Average Position.” A major dip in the graph represents that your positions have potentially been shaken.
Review the trend for top pages and queries to see which ones dropped. A minor drop in position (from position 2 to 5) is common post-update behavior, whereas a major drop (from position 4 to 30) indicates an underlying cause.
How to Fix It
Identify pages with the highest drop rate and assess them separately. Find target keywords for each and manually search them on Google to review which pages show up. A deeper competitor assessment will help identify the ranking signals your competitors are getting rewarded for that you may have overlooked. Maybe it’s content quality and structure, maybe it’s their backlinks, or a better user experience.
Run an audit to see what your pages are lacking and optimize them to reclaim lost positions.
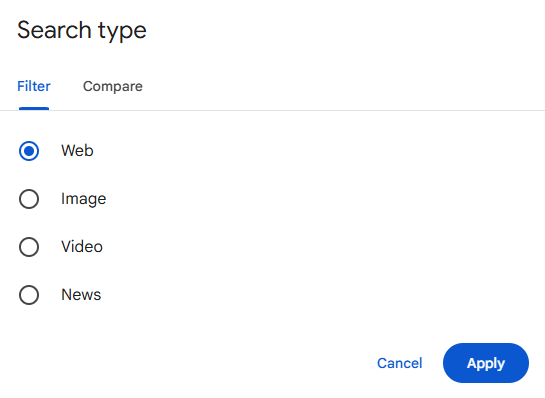
Distinguish Performance by Search Type
Filter the performance report for different search types to assess which one incurred the greatest impact on your performance. Google Search Console lets you view data based on Web, Video, News, and Images. Identify which search type displays the highest drop in impressions, traffic, and positions, then craft a strategy to apply targeted action.
How to Fix It
Depending on where the drop happens, here’s what you can do.
Web: Identify pages and fix content, speed, UX, or other diagnosed factors.
Images: Optimize file types, file names, apply alt text, use appropriate schema, and assess images for quality.
News: Make sure you’re using the right headlines, incorporating keywords, and creating authoritative content. It’s also important to implement structured data, use media-rich content, and fix technical issues.
Video: Assess whether it’s the content quality or a technical error causing the drop and address it accordingly.
Important! It’s vital to note that these are generic guidelines, and it’s essential to first diagnose the root cause of a drop before taking any action.
Broad Core Updates Vs. Small Updates: What’s the Difference?
So there are the larger core updates in which Google recalibrates the entire ranking system, and there are the smaller named updates, which often target one aspect of the search.
For example, if a core update is analogous to renovating an entire building, a targeted update would be like fixing one aspect of every room in that building—cracked walls, chipping paint, or floor epoxy. Think of the 2011 Panda update that targeted websites using content farms, excessive ads, and those that were generally low-value for users. On the other hand, core updates modify ranking factors and cause significant volatility across the SERPs. They’re not mere tremors across pages, but a full-blown shakeup of the search landscape.
Google Search Central states:
“We’re continually making updates to our search algorithms, including smaller core updates.”
Named updates like Helpful Content Update and the Penguin Update often become part of the Google core algorithm. They help regulate the ranking system and satisfy search intent.
One thing broad core updates are not is a manual penalty. They are used to justify ranking positions, but they don’t target specific sites. That happens with named updates focusing on one particular aspect of the algorithm. That said, there are other differences between broad core updates and smaller updates.
Difference Between Broad Core Updates & Small Core Updates
Timeline – Core updates are always announced from the start to end dates, whereas targeted updates are not. Often, SEOs recognize them by tracking data from multiple sites to determine changes and targeted impact.
Recovery — Since targeted updates rely on targeted action, it’s easy to determine and address the issue, like changing content, building better backlinks, or improving page speed. With broad core updates, the algorithm re-evaluates your entire site. This needs a holistic approach and site-wide analysis to review negative patterns and fix them.
Scope of Impact – Core update impact can span 5% to 10% of searches, while smaller updates affect no more than 1%.
Have Broad Core Updates Become More Frequent?
That leaves us with one last speculation: have broad core updates been rolling out more frequently over time? And the answer is in the rollout patterns witnessed in the past years.
| Year | List of Broad Core Updates |
| 2025 | December 2025 core update |
| 2024 | December 2024 core update
November 2024 core update |
| 2023 | November 2023 core update
October 2023 core update August 2023 core update March 2023 core update |
| 2022 | September 2022 core update |
| 2021 | November 2021 core update
July 2021 core update June 2021 core update |
What the table represents
This table reflects inconsistent patterns, with some years highlighting more updates than others. But what matters is what SEOs and marketers should be doing to stay afloat through both broad core updates and targeted updates.
The simple answer is consistency. With Google claiming continuous adjustments of the ranking algorithm via small core updates, websites should swear by three key practices.
- Strengthening topical authority with helpful, people-first content, following EEAT guidelines, and linking internally.
- Focusing on organic linking via quality content that people want to refer to. A strong backlink profile can get sites one step ahead in their journey to page one.
- Improving user experience and fixing technical errors as soon as they appear.
A gap of four to five months between core updates corroborates that small core updates happen on an ongoing basis. This was documented in the latest Google updates section.
“Added information to the core updates documentation about how Google continually makes updates to our search algorithms (including smaller core updates), and how that can affect your website.”
So besides the broader core updates, there are continuous ranking changes, a.k.a., the unannounced updates. They happen regularly and may impact your rankings even if changes are made far from announced core update timelines.
So the answer to whether there have been more core updates would be a negative. But does that mean you are safe? That’s a no. What works is following best practices and working on brand building rather than implementing manipulative techniques to artificially meet the ranking factors.
Just last year alone, there was a five-month difference between the June Core update and December core update. That’s a sign not to expect frequent updates, but rather a consistent stream of ranking changes that happen automatically across the algorithm.
The Final Analysis
That’s it, folks. This was our version of a complete account of what broad core updates are, how to analyze their impact, and how to recover from them. We’ve seen many updates happen that reward sites and others that significantly penalized black hat SEO practices. The cycle will continue, but sites consistently producing quality content, organic backlinks, and ensuring users get the best experience will always remain true winners in the SEO marathon.